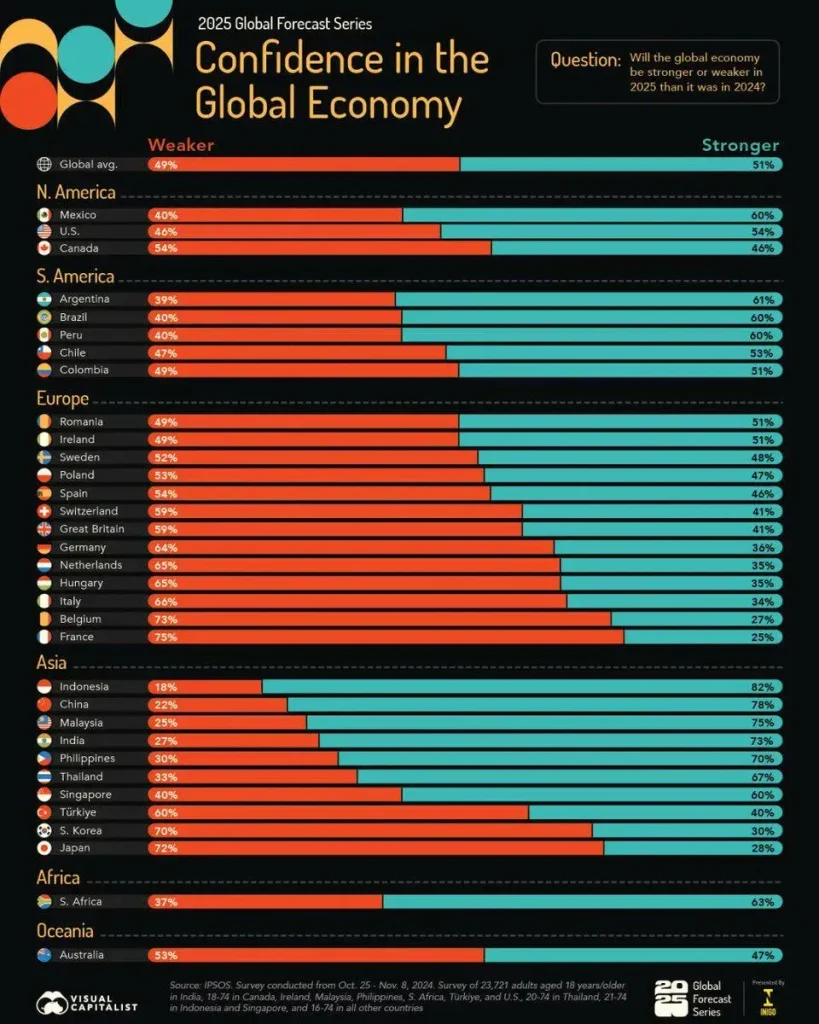
Global economy in 2025 is shaping decisions for savers, investors, and policymakers, blending resilience with new sources of uncertainty. As you explore 2025 economic trends and the inflation outlook 2025, you will see how growth paths, policy calibrations, and technology shifts influence everyday budgets. The piece also highlights how global markets 2025 react to policy impacts 2025, delivering practical implications for savings, debt, and investment timing. By tying macro forces to household and business choices, the analysis translates complex trends into concrete steps you can take. In a world of uneven growth and policy trade-offs, readers gain a clearer roadmap for navigating risk and seizing opportunities.
Viewed through an international macro lens, the year ahead is a tapestry of varied growth rates, shifting inflation dynamics, and policy posture signals that influence markets, households, and firms. Other terms to describe the landscape include the global economic outlook, cross-border trade patterns, and the digital transformation of work. The sense of momentum depends on productivity gains, investment in skills, and the pace of energy transition. By reframing the topic with terms like macroeconomics in flux, regional growth differentials, and monetary and fiscal policy trajectories, readers can map opportunities and risks more clearly.
Global economy in 2025: Inflation, policy shifts, and growth
Global economy in 2025 presents a patchwork of resilience and turbulence. Growth is likely uneven across regions, with advanced economies contending with tighter credit conditions and productivity challenges, while some emerging markets benefit from reform agendas and commodity cycles. The inflation outlook 2025 remains a moving target as energy prices, wage dynamics, and services inflation interact with shifting global demand. Central banks face a careful trade-off: tighten enough to anchor expectations without choking off growth, aiming for a gradual policy normalization that supports recovery and confidence.
From a practical perspective, these macro dynamics translate into tangible outcomes for households and businesses. Policy impacts 2025 will influence borrowing costs, mortgage rates, and the affordability of major purchases, making it essential to monitor inflation indicators and central-bank guidance. The global markets 2025 environment underscores the value of diversified portfolios that span equities, bonds, and alternatives, while remaining attuned to sector sensitivities and regional growth differentials. As supply chains realign and the energy transition accelerates, price pressures and investment opportunities will hinge on how policymakers, firms, and households respond to evolving growth trajectories.
Global economy in 2025: Preparation for households and businesses
For households, the 2025 outlook translates into concrete budgeting and planning choices. The inflation outlook 2025 suggests real purchasing power may fluctuate, so prioritizing essential spending, building an emergency fund, and reviewing debt levels—along with refinancing when favorable—can improve resilience. Investing in skills and education remains a practical hedge against labor-market shifts driven by automation and AI-enabled productivity gains, helping individuals position themselves for higher-demand roles in a changing economy.
Businesses and investors can align strategy with the evolving macro landscape by strengthening supply-chain resilience, rebalancing supplier networks, and adopting digital tools that boost efficiency. The energy transition and evolving trade policies will influence cost structures and export dynamics, making scenario planning and cash-flow stress tests increasingly important. For savers and long-term planners, a thoughtful allocation across global markets 2025—including equities, bonds, and alternatives—can help balance policy impacts 2025 with growth potential, while reducing vulnerability to volatility and policy surprises.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key 2025 economic trends for the Global economy in 2025, and how does the inflation outlook 2025 affect households?
The Global economy in 2025 is expected to show uneven growth across regions as policymakers balance inflation with demand and supply pressures. The inflation outlook 2025 remains uncertain, driven by energy prices, wage dynamics, and services inflation, with central banks likely pursuing gradual policy normalization to anchor expectations without derailing activity. For households, this means watching interest rates, borrowing costs, and price movements that affect saving and big-ticket purchases. Keeping an eye on these macro trends helps with budgeting, debt management, and long‑term planning.
How do policy impacts 2025 and global markets 2025 shape investment decisions in the Global economy in 2025?
Policy impacts 2025, including tighter monetary conditions and prudent fiscal posture, can influence borrowing costs, corporate investment, and consumer credit within the Global economy in 2025. Global markets 2025 may experience bouts of volatility as investors react to policy signals and geopolitical developments, so diversification across equities, bonds, and alternatives can help manage risk. Investors should align portfolios with the inflation outlook 2025, anticipated growth differentials, and the pace of policy normalization, while staying prepared for potential rate moves and market shifts.
| Topic | Key Points | Implications for Households | Implications for Businesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Growth trajectory and regional variation | Global growth is uneven; advanced economies balance credit conditions and productivity gains; 2025 may see gradual stabilization; pace depends on policy response to inflation, supply bottlenecks, and geopolitical frictions. | Job prospects and consumer demand may vary by region; households should monitor demand trends and adjust spending/savings. | Plan for diversified demand, slower but steadier expansion in some regions; adapt investment horizons to policy and demand shifts. |
| Inflation and policy posture | Inflation remains a moving target as energy, wages, and services inflation interact with global demand; central banks face a trade-off between policy tightening and growth; gradual policy normalization expected; credit costs and mortgage rates will influence affordability. | Households face higher or fluctuating borrowing costs and budgeting challenges; savings behavior may shift. | Financing costs, mortgage rates, and consumer demand influence pricing strategies and investment plans; maintain balance-sheet resilience. |
| Global markets and capital flows | Markets may experience episodes of volatility; earnings signals, geopolitics, and policy shifts drive risk/reward; broader macro resilience could support equities, bonds, and alternatives if growth stays steady. | Diversified portfolios and risk management; focus on liquidity and long-term goals. | Access to capital remains important; align investments with macro cycles and stay mindful of asset-class sensitivity to policy and growth differentials. |
| Supply chains, trade, and energy transition | Supply chains realignments; tariffs and sanctions considerations; energy markets and transition affect inflation and sectoral growth; regional comparative advantages shift. | Households may face prices and energy costs; adaptation to new energy realities affects consumption patterns. | Firms should diversify supplier networks and manage energy risk; adjust export/import strategies and capital expenditure to energy-transition implications. |
| Labor markets, technology, and productivity | Automation, digitalization, and AI-enabled services offer productivity gains but raise displacement and wage dynamics; resilience depends on reskilling and education investments. | Individuals may pursue upskilling and career planning; wage growth may vary by sector. | Businesses should attract/retain skilled workers and leverage technology to boost efficiency and resilience. |
| What 2025 means for households and businesses | Budgeting should factor potential shifts in interest rates, tax policy, and consumer prices; debt, refinancing, and long-term savings need review; near-term risks vs longer-term opportunities acknowledged. | Review debt levels, refinancing options, and long-term savings goals; plan cash flow and resilience. | Small businesses should assess cash flow, inventory strategies, and investment plans; weigh near-term risks against growth opportunities. |
| Strategic takeaways | Diversify investments across asset classes; monitor inflation and central bank guidance; invest in skills; consider energy and trade developments; build an emergency fund and flexible financial plan. | Apply these takeaways to household budgeting and saving decisions; maintain readiness for policy shifts. | Incorporate these strategies into capital allocation, risk management, and financial planning for 2025 and beyond. |
Summary
Conclusion: A concise recap follows the table. Global economy in 2025 carries potential and uncertainty, shaped by how growth unfolds across regions, inflation trends, policy responses, and the pace of the energy transition. The key forces—growth trajectories, inflation dynamics, policy settings, and the balance between technology and labor—will influence household finances and business decisions. By staying informed and planning with flexibility, readers can navigate 2025’s volatility, capitalize on opportunities, and build resilience through prudent saving, investing, and risk management. The interconnected nature of global markets and local conditions means proactive preparation can turn macro volatility into a pathway for growth and stability.