Global economy in 2025 is shaped by interlinked forces that challenge policymakers, businesses, and households across economies and sectors. Across regions, policy normalization, moderating inflation, and rapid digital change shape the year ahead. Analysts see uneven growth, with some economies stabilizing while others accelerate, reflecting a mixed economic landscape. Geopolitical risks 2025, evolving trade patterns, and energy-price swings remind firms to diversify and build buffers. That context makes resilient supply chains essential, prompting onshoring, smarter inventories, and flexible supplier networks.
From a broader macro lens, the year ahead outlines a world economy trajectory shaped by policy, markets, and technology. This framing emphasizes macro outlook, regional growth dynamics, and cross-border shifts as signals guiding investment. Policy choices, capital flows, and resilience will set the pace of expansion through 2025.
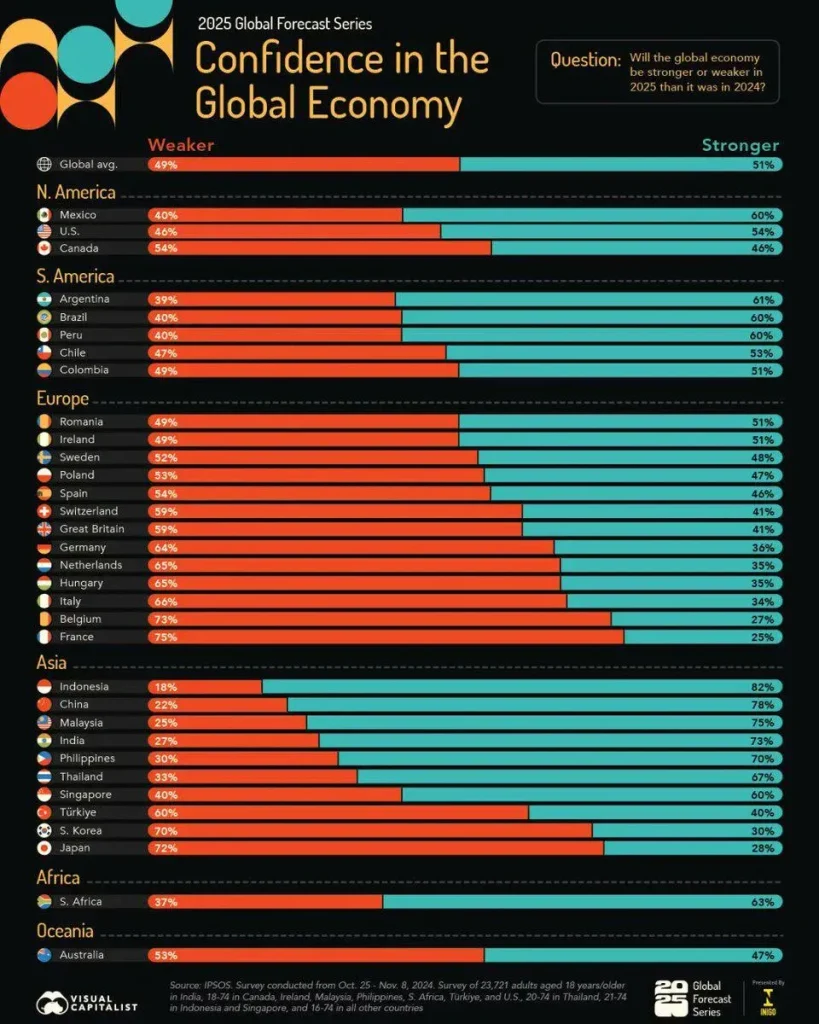
Global economy in 2025: Navigating monetary policy normalization, inflation dynamics, and geopolitical risks
The global economy in 2025 unfolds as a web of interconnected drivers—monetary policy normalization, inflation that remains higher than pre-pandemic trends in several regions, rapid digital transformation, and a shifting energy landscape. This dynamic aligns with the economic outlook 2025, which anticipates uneven growth across regions: steadier expansion in advanced economies alongside pockets of faster growth in certain emerging markets, driven by demographics, infrastructure investment, and evolving trade links. In this context, the global economy 2025 resembles a complex system where policy choices ripple through supply chains, capital markets, and labor markets.
For policymakers, businesses, and households, resilience is the core objective. The inflation forecast 2025 suggests a cautious path for interest rates and monetary support, while energy prices and trade patterns continue to shape demand. Companies increasingly prioritize diversified sourcing, regionalized supply chains, and robust risk analytics to protect margins. Emphasizing supply chain resilience 2025—through better visibility, inventory management, and instrumented supplier networks—becomes a practical way to cushion against geopolitical risks 2025 and other cross-border shocks.
Opportunities and strategic imperatives for 2025: AI, green infrastructure, and diversified supply chains
The 2025 landscape presents opportunities across green energy, infrastructure, and the climate economy. Investments in renewables, grid modernization, storage, and climate adaptation can unlock durable demand, create jobs, and spur regional growth consistent with the global economy in 2025. At the same time, the digital economy and AI-enabled productivity offer meaningful gains in manufacturing, logistics, and services, enabling firms to improve efficiency, tailor offerings, and shorten time-to-market in a competitive global arena.
Yet opportunities come with vulnerabilities. Energy price volatility, debt sustainability concerns, and climate risks require prudent planning and scenario analysis. Regions with advanced digital capabilities and resilient supply chains will be better positioned to capitalize on gains from the economic outlook 2025, even as geopolitical risks 2025 and shifting trade patterns demand agile strategies. Emphasizing supply chain resilience 2025—through diversification, nearshoring, and smarter inventory—helps safeguard growth and sustain momentum in the global economy 2025.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key forces driving the global economy in 2025?
The global economy in 2025 is shaped by monetary policy normalization and inflation dynamics, with the inflation forecast 2025 showing a decline from post-pandemic highs but remaining above trend in several regions. Digitalization and AI-enabled productivity are lifting potential growth, while the energy transition and climate policies influence investment, pricing, and policy settings. Demographics and labor markets, alongside geopolitical risks 2025, help explain why growth remains uneven across regions. This pattern aligns with the economic outlook 2025, highlighting how policy choices ripple through supply chains, capital markets, and labor markets, creating both opportunities and vulnerabilities.
What opportunities and risks should businesses monitor in the global economy in 2025?
Opportunities in the global economy in 2025 include green energy, infrastructure, and climate-related investments that spur demand and job creation, plus the digital economy and AI-enabled productivity that boost efficiency. Companies can strengthen supply chain resilience 2025 by onshoring, nearshoring, and diversifying suppliers to reduce disruption and lower costs over time. At the same time, risks such as inflation forecast 2025 volatility, geopolitical risks 2025, energy price swings, and debt sustainability require prudent risk management. Firms should use scenario planning and diversify markets to balance opportunities with these risks.
| Key Theme | What It Means | Implications / Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Monetary policy normalization and inflation dynamics | Central banks recalibrate to stabilize prices while supporting sustainable growth; inflation remains above trend in some regions. | Influences interest rates, consumer spending, and business investment; pricing of risks across sectors. |
| Digitalization and productivity gains | Accelerated digital services, cloud computing, and AI-driven optimization raise productivity. | Potential for higher long-run growth and stronger margins; firms benefit from data-driven decision-making. |
| Energy transition, climate policy, and commodity dynamics | Shift toward cleaner energy; energy prices and policy support shape capital expenditure and inventories. | Regional differences in energy endowments and transition costs affect inflation and growth trajectories. |
| Demographics and labor markets | Aging populations, urbanization, and changing skill needs reshape supply of labor and demand for wages. | Offsets supply constraints and supports inclusive growth through reforms and retraining. |
| Geopolitical tensions and trade patterns | Sanctions dynamics, regional conflicts, and shifts in global trade networks influence investment and supply chains. | Encourages diversification, regionalization of production, and heightened risk assessment by firms. |
| Opportunities: Green energy, infrastructure, and the climate economy | Investments in renewables, grid modernization, storage, and climate adaptation create demand across sectors. | Potential job creation and regional growth with spillovers to related industries. |
| Opportunities: Digital economy and AI-enabled productivity | Widespread AI, automation, and analytics enable efficiency gains and new markets for digital services. | Faster time-to-market, personalized customer experiences, and new business models. |
| Opportunities: Resilient and diversified supply chains | Onshoring, nearshoring, and regionalization reduce vulnerability to shocks. | Lower disruption costs and more robust margins over time through diversified sourcing. |
| Opportunities: Healthcare, demographics, and consumer demand | Advances in biotech, diagnostics, and elder care align with aging populations. | Growing markets for pharmaceuticals, devices, and care services with stable demand. |
| Opportunities: Emerging markets as growth engines | Improved political stability, education investment, and expanding middle classes. | Broader participation in global value chains and increased cross-border investment. |
| Risks: Inflation persistence and policy missteps | Inflation may persist due to shocks or delayed policy responses; inflation trajectory is uncertain. | Impacts investment, pricing, and consumer confidence; policy credibility matters. |
| Risks: Debt sustainability and financial fragility | Elevated leverage raises vulnerability to rising rates and growth slowdowns. | Requires prudent debt management, fiscal rules, and transparent risk disclosure. |
| Risks: Energy price volatility and commodity cycles | Fluctuations in energy markets affect costs, inflation, and competitiveness. | Hedging, diversification, and policy coordination help dampen volatility. |
| Risks: Geopolitical and trade risk | Escalating tensions or sanctions can disrupt supply chains and financial markets. | Scenario planning, regional diversification, and robust risk management are prudent. |
| Risks: Climate risk and environmental shocks | Extreme weather and climate events threaten infrastructure and production. | Incorporate climate risk into investment decisions and resilience planning. |
| Policy and business strategy | Coordinate monetary, fiscal, energy, trade, and environmental policies; invest in capabilities. | Build resilience, raise productivity, and pursue inclusive growth across regions. |