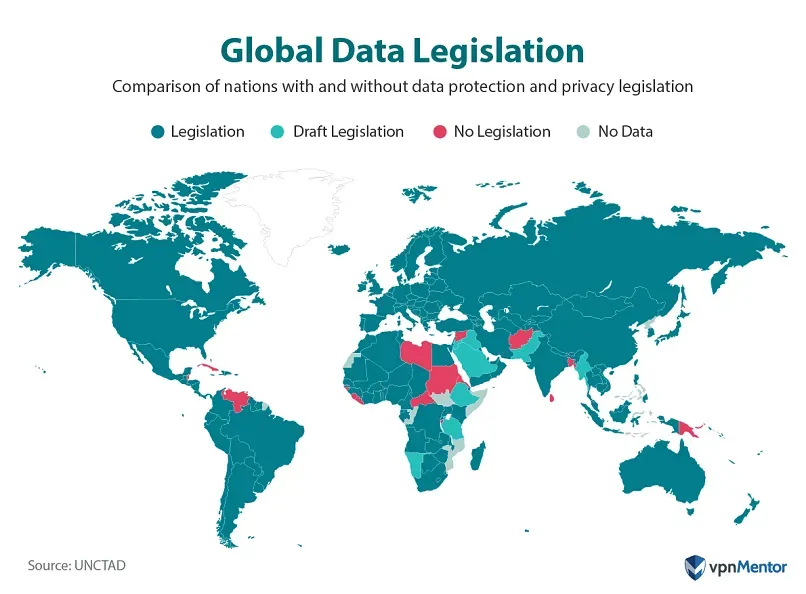
Global data privacy has moved from a niche legal topic to a central business priority. As data collection grows across cloud services and digital platforms, organizations face a patchwork of rules and increasingly stringent enforcement. The aim is to build trust with customers, partners, and employees while enabling responsible innovation rather than merely avoiding penalties. This article surveys the regulatory landscape and highlights GDPR compliance as a benchmark for global privacy programs. It also outlines practical steps to integrate privacy into governance and operations through clear rights management, transparency, and risk-based controls.
From a global perspective, privacy concerns span cross-border data transfer rules, data protection standards, and risk-based governance. Rather than a checkbox exercise, privacy becomes a design principle—privacy by design—embedded in products, services, and processes. Organizations should map data flows, implement consent-aware processes, and maintain transparent user rights across jurisdictions. Regulatory trajectories are moving toward convergence, yet local nuances continue to shape how data is stored, used, and safeguarded. A resilient privacy program uses governance, technology, and culture to protect personal information while enabling sustainable innovation.
Global data privacy: Navigating Global Data Privacy Regulations and GDPR Compliance for Modern Businesses
Organizations today must align with a complex landscape of global data privacy regulations. The GDPR sets a high standard for lawful bases, data subject rights, and security, shaping compliance expectations across markets. Building a program that maps data flows, conducts DPIAs, and maintains Records of Processing Activities becomes essential to demonstrate GDPR compliance while addressing regional variations. Understanding cross-border data transfer rules, including SCCs and adequacy decisions, helps ensure data can move securely while preserving privacy protections. In practice, framing policies around data protection and privacy laws provides a solid foundation for risk management and trust-building with customers, partners, and regulators.
Adopting a unified privacy program that transcends local rules requires governance that links policy, people, and technology. This entails comprehensive data inventory, data minimization, and transparent notices that reflect the expectations of global data privacy regulations. Emphasizing privacy by design and by default reduces risk upfront, enabling scalable compliance with GDPR compliance and other regimes. By treating privacy as a strategic asset rather than a checkbox exercise, organizations can balance innovation with accountability and build lasting trust in a global customer base.
Implementing Privacy by Design Across Cross-Border Data Transfer Rules and Data Protection and Privacy Laws
To operationalize privacy, organizations should embed privacy by design into product development, data processing workflows, and vendor management. This approach aligns with data protection and privacy laws and helps demonstrate accountability under global frameworks while addressing cross-border data transfer rules. By integrating privacy considerations from the earliest design stage, teams minimize data collection, apply purpose limitation, and implement strong access controls that support safe data flows across regions. A mature program also documents processing activities and maintains risk-based security measures to satisfy regulatory expectations.
Beyond technical controls, governance and culture are critical. Training, incident response planning, and ongoing risk assessments ensure that privacy by design remains at the core of daily operations. When privacy becomes part of the architecture, it supports scalable GDPR compliance and helps sustain trust with customers as data crosses borders. Aligning cross-border data transfer rules with SCCs, adequacy decisions, and supplementary measures ensures ongoing compliance as regulatory guidance evolves, while data protection and privacy laws shape vendor contracts and due diligence.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do global data privacy regulations influence GDPR compliance for multinational organizations?
Global data privacy regulations shape GDPR compliance by demanding accountability, data mapping, and risk-based security across borders. A multinational privacy program should implement a unified framework that includes data inventory, DPIAs for high-risk processing, and Records of Processing Activities, while aligning cross-border transfers with mechanisms like SCCs and adequacy decisions to support GDPR compliance. This approach helps demonstrate GDPR compliance, reduces risk, and builds trust with customers and regulators.
Why are cross-border data transfer rules and privacy by design central to meeting data protection and privacy laws?
Cross-border data transfer rules ensure that personal data remains protected when moved between jurisdictions, while privacy by design embeds privacy protections into products and processes from the start. Implementing SCCs and assessing adequacy for transfers, along with privacy by design and default, data minimization, and clear notices, helps meet data protection and privacy laws and supports responsible global operations.
| Aspect | Key Points | Examples / Details |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Landscape | Global principles and major regimes | GDPR as benchmark; US sectoral laws (HIPAA, CPRA); cross-border transfer rules (SCCs); other regimes (LGPD, PIPL, PDPA, POPIA) |
| Compliance Frameworks & Governance | Governance, data handling, and risk management | Data inventory and mapping; privacy by design and default; DPIAs; rights management; security controls; third‑party risk; incident response |
| Trust, Transparency & Rights | Transparency, user control, and accountability | Privacy by design; least privilege; security culture; accountability mechanisms |
| Practical Implementation | Actionable steps to build a privacy program | Data audits; map data flows; DPIA framework; rights processes; robust security; vendor management; cross-border transfers; governance & training; measure progress |
| Future Trends | Emerging patterns and challenges | AI explainability; regulatory convergence vs fragmentation; stronger enforcement; privacy by default; data localization |
Summary
Global data privacy is a dynamic and strategic area that touches every aspect of modern business. The most successful privacy programs balance compliance with risk management and customer trust. By understanding global data privacy regulations, implementing robust governance, and embedding privacy by design into products and processes, organizations can minimize risk, accelerate data-driven innovation, and foster long-term trust with stakeholders. As regulations evolve and technology advances, a proactive, transparent, and principled approach to data protection will remain essential for sustainable growth and competitive differentiation.