The Post-Pandemic Economy marks a critical shift from emergency relief to resilient, long-term growth. It blends changes in consumer behavior, business investment, and policy choices to chart recovery pathways after the pandemic, including post-pandemic economic recovery. As inflation and growth post-pandemic dynamics emerge, policymakers balance stabilization with productivity gains. The focus is on sustainable renewal, with macroeconomic policy post-pandemic guiding investment, skills development, and stronger supply chains, alongside policy shifts after COVID-19. By framing opportunities and risks together, this framework invites dialogue on inclusive growth and shared prosperity.
Viewed through the lens of a post-crisis rebound, this era centers on policy calibration and durable productivity. The economic recovery trajectory after the pandemic blends digital acceleration, workforce upskilling, and smarter capital allocation. Additionally, adjustments in fiscal and monetary stances—such as targeted incentives and steady price signals—support resilient expansion. In this new normal, terms like post-pandemic recovery, sustainable revival, and structural reform describe the same phenomenon in different contexts.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Post-Pandemic Economy and what are the recovery pathways after the pandemic?
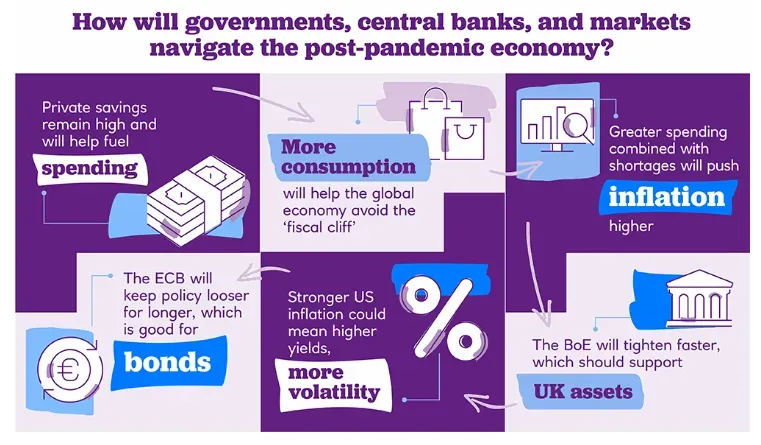
The Post-Pandemic Economy describes the economic environment after COVID-19, shaped by consumer demand, investment, technology adoption, and policy choices. Recovery pathways after the pandemic typically include: a demand-driven rebound as real incomes recover; an investment-led upturn driven by digital, green, and infrastructure investments; productivity and innovation gains from automation and skills development; and sectoral realignment to strengthen resilience and supply chains. Policymakers combine targeted fiscal support with prudent monetary policy and structural reforms to sustain inflation within target ranges, support sustainable growth, and manage public debt in the post-pandemic era.
What policy shifts after COVID-19 are most effective for inflation and growth in the Post-Pandemic Economy?
Policy shifts after COVID-19 that support inflation control and growth typically blend fiscal, monetary, and structural reforms. Key elements include targeted infrastructure and green investments to boost productivity; tax incentives for R&D and upskilling to accelerate innovation; selective spending that sustains jobs while protecting debt sustainability; monetary policy normalization and strong financial stability to anchor inflation expectations; and inclusive social protection programs that support human capital and demand. Together, these macroeconomic policy post-pandemic steps balance price stability with investment, productivity gains, and broad-based growth in the inflation-and-growth post-pandemic context.
| Section | Key Points | Implications / Outlook |
|---|---|---|
| Recovery Pathways in the Post-Pandemic Economy |
|
|
| Policy Shifts and Their Impacts |
|
|
| Macro-Financial Dynamics: Inflation, Growth, and Public Debt |
|
|
| Global Considerations and Sectoral Realities |
|
|
| Skills, Workforce, and Human Capital |
|
|
| Risks, Uncertainties, and Policy Adaptation |
|
|
Summary
Post-Pandemic Economy is a landscape of cautious optimism, where recovery pathways blend demand revival, investment-led growth, and productivity gains to lay the groundwork for sustainable prosperity. The pathways are diverse and interdependent, requiring a balanced mix of policy support for consumption, investment, and innovation. Policy shifts—fiscal investments aligned with productivity, targeted incentives, prudent monetary normalization, and inclusive social programs—shape the trajectory by sustaining potential output while maintaining macro stability. Inflation, debt sustainability, and global dynamics remain central considerations guiding policy calibration and risk management. A durable post-pandemic renewal rests on robust human capital development, sectoral diversification, resilient supply chains, and institutions capable of sustaining higher living standards for all citizens.